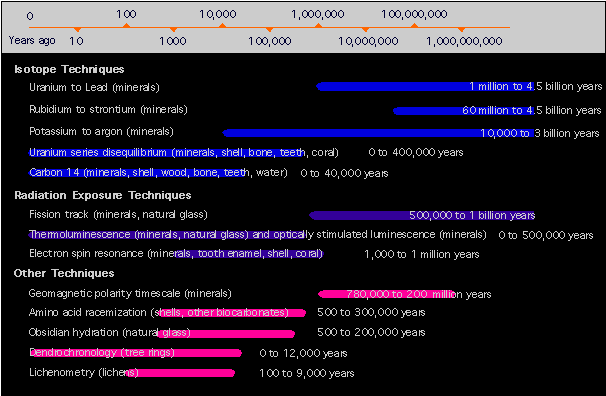
The absolute age of a wide variety of rocks, fossils, and human artifacts can be determined by various laboratory procedures. Deciding which test to perform depends on the composition and believed approximate age of a particular specimen. For example Carbon 14 is often the method of choice for scientists dating organic artifacts like wood, charcoal, bone, and teeth that are less than about 40, years.
Log in or sign up to add this lesson to a Custom Course. Login or Sign up. Gillaspy has taught health science at University of Phoenix and Ashford University and has a degree from Palmer College of Chiropractic. The aging process in human beings is easy to see. As we age, our hair turns gray, our skin wrinkles and our gait slows.
You must create an account to continue watching
However, rocks and other objects in nature do not give off such obvious clues about how long they have been around. So, we rely on radiometric dating to calculate their ages. Radiometric dating, or radioactive dating as it is sometimes called, is a method used to date rocks and other objects based on the known decay rate of radioactive isotopes.
Different methods of radiometric dating can be used to estimate the age of a variety of natural and even man-made materials.
- free dating site calgary alberta.
- Radiometric dating?
- ?
The methods work because radioactive elements are unstable, and they are always trying to move to a more stable state. So, they do this by giving off radiation. This process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by releasing radiation is called radioactive decay. The thing that makes this decay process so valuable for determining the age of an object is that each radioactive isotope decays at its own fixed rate, which is expressed in terms of its half-life.
So, if you know the radioactive isotope found in a substance and the isotope's half-life, you can calculate the age of the substance. So, what exactly is this thing called a half-life? Well, a simple explanation is that it is the time required for a quantity to fall to half of its starting value. So, you might say that the 'full-life' of a radioactive isotope ends when it has given off all of its radiation and reaches a point of being non-radioactive.
When the isotope is halfway to that point, it has reached its half-life. There are different methods of radiometric dating that will vary due to the type of material that is being dated.
Radiometric dating - Wikipedia
For example, uranium-lead dating can be used to find the age of a uranium-containing mineral. It works because we know the fixed radioactive decay rates of uranium, which decays to lead, and for uranium, which decays to lead So, we start out with two isotopes of uranium that are unstable and radioactive. They release radiation until they eventually become stable isotopes of lead.
These two uranium isotopes decay at different rates.
In other words, they have different half-lives. The half-life of the uranium to lead is 4. The uranium to lead decay series is marked by a half-life of million years. These differing rates of decay help make uranium-lead dating one of the most reliable methods of radiometric dating because they provide two different decay clocks.
- difference between dating and boyfriend girlfriend.
- Radiometric Dating?
- deutsche dating seite kostenlos.
This provides a built-in cross-check to more accurately determine the age of the sample. Uranium is not the only isotope that can be used to date rocks; we do see additional methods of radiometric dating based on the decay of different isotopes. For example, with potassium-argon dating , we can tell the age of materials that contain potassium because we know that potassium decays into argon with a half-life of 1.
Navigation menu
With rubidium-strontium dating , we see that rubidium decays into strontium with a half-life of 50 billion years. By anyone's standards, 50 billion years is a long time. In fact, this form of dating has been used to date the age of rocks brought back to Earth from the moon. So, we see there are a number of different methods for dating rocks and other non-living things, but what if our sample is organic in nature? For example, how do we know that the Iceman, whose frozen body was chipped out of glacial ice in , is 5, years old? Well, we know this because samples of his bones and hair and even his grass boots and leather belongings were subjected to radiocarbon dating.
Radiocarbon dating , also known as carbon dating or simply carbon dating, is a method used to determine the age of organic material by measuring the radioactivity of its carbon content. So, radiocarbon dating can be used to find the age of things that were once alive, like the Iceman. And this would also include things like trees and plants, which give us paper and cloth.
Radiometric Dating: Methods, Uses & the Significance of Half-Life
So, radiocarbon dating is also useful for determining the age of relics, such the Dead Sea Scrolls and the Shroud of Turin. With radiocarbon dating, the amount of the radioactive isotope carbon is measured. Compared to some of the other radioactive isotopes we have discussed, carbon's half-life of 5, years is considerably shorter, as it decays into nitrogen Carbon is continually being created in the atmosphere due to the action of cosmic rays on nitrogen in the air. Carbon combines with oxygen to create carbon dioxide. Because plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, this isotope ends up inside the plant, and because animals eat plants, they get some as well.
When a plant or an animal dies, it stops taking in carbon The existing carbon within the organism starts to decay back into nitrogen, and this starts our clock for radiocarbon dating. A scientist can take a sample of an organic material when it is discovered and evaluate the proportion of carbon left in the relic to determine its age. Radiometric dating is a method used to date rocks and other objects based on the known decay rate of radioactive isotopes. The decay rate is referring to radioactive decay , which is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by releasing radiation.
When Rutherford announced his findings it soon became clear that Earth is millions of years old. These scientists and many more after them discovered that atoms of uranium, radium and several other radioactive materials are unstable and disintegrate spontaneously and consistently forming atoms of different elements and emitting radiation, a form of energy in the process.
The original atom is referred to as the parent and the following decay products are referred to as the daughter. Carbon is a very special element. In combination with hydrogen it forms a component of all organic compounds and is therefore fundamental to life. Libby of the University of Chicago predicted the existence of carbon before it was actually detected and formulated a hypothesis that radiocarbon might exist in living matter.
Willard Libby and his colleague Ernest Anderson showed that methane collected from sewage works had measurable radiocarbon activity whereas methane produced from petroleum did not. Perseverance over three years of secret research to develop the radiocarbon method came into fruition and in Libby received the Nobel Prize for chemistry for turning his vision into an invaluable tool.
Carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes , with atoms of the same atomic number but different atomic weights. They are 12 C, 13 C and 14 C. C being the symbol for carbon and the isotopes having atomic weights 12, 13 and The three isotopes don't occur equally either, The radiocarbon dating method is based on the rate of decay of the radioactive or unstable 14 C which is formed in the upper atmosphere through the effect of cosmic ray neutrons upon nitrogen The reaction is as follows: After formation the three carbon isotopes combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
The carbon dioxide mixes throughout the atmosphere, dissolves in the oceans, and via photosynthesis enters the food chain to become part of all plants and animals. In principle the uptake rate of 14 C by animals is in equilibrium with the atmosphere. As soon as a plant or animal dies, they stop the metabolic function of carbon uptake and with no replenishment of radioactive carbon, the amount of 14 C in their tissues starts to reduce as the 14 C atoms decay.
Libby and his colleagues first discovered that this decay occurs at a constant rate. They found that after years, half the 14 C in the original sample will have decayed and after another years, half of that remaining material will have decayed, and so on. This became known as the Libby half-life.