It is used to date organic materials less than 70, years old. Switch to new thesaurus. References in periodicals archive? In the past the only way to date landslides in a given area was through the time-consuming and expensive process of radiocarbon dating rocks from a debris field. Innovative system helping identify landslide risks. Based on radiocarbon dating of animal bones he found in the caves, he proposed humans had settled in the area as far back as 30, years ago. Cutting-edge nuclear techniques help prove Australia's oldest Aboriginal site.
Researchers used radiocarbon dating to determine the ages of 28 of the animals, and estimated that one female was about years old. Radiocarbon dating of twigs, seeds and plant fragments from submerged sediment layers provides a solid age estimate for six stone artifacts excavated by scuba divers. Florida inhabited surprisingly early: Radiocarbon dating carried out in July concluded that the manuscript may be at least 1, years old, meaning that it was written--at the latest years after the death of the prophet Muhammad.
Since the technique was first developed in the late s, radiocarbon dating has become an essential tool for researchers in the fields of archaeology, forensics, earth science, and art forgery detection, among many other disciplines. Radiocarbon dating puts the man's death at between and AD. Radiocarbon dating has allowed key transitions in prehistory to be dated, such as the end of the last ice age , and the beginning of the Neolithic and Bronze Age in different regions. In , Martin Kamen and Samuel Ruben of the Radiation Laboratory at Berkeley began experiments to determine if any of the elements common in organic matter had isotopes with half-lives long enough to be of value in biomedical research.
They synthesized 14 C using the laboratory's cyclotron accelerator and soon discovered that the atom's half-life was far longer than had been previously thought. Korff , then employed at the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia , that the interaction of thermal neutrons with 14 N in the upper atmosphere would create 14 C. In , Libby moved to the University of Chicago where he began his work on radiocarbon dating. He published a paper in in which he proposed that the carbon in living matter might include 14 C as well as non-radioactive carbon.
By contrast, methane created from petroleum showed no radiocarbon activity because of its age. The results were summarized in a paper in Science in , in which the authors commented that their results implied it would be possible to date materials containing carbon of organic origin. Libby and James Arnold proceeded to test the radiocarbon dating theory by analyzing samples with known ages.
- Sign up, it's free!.
- radiocarbon dating;
- best dating website leeds.
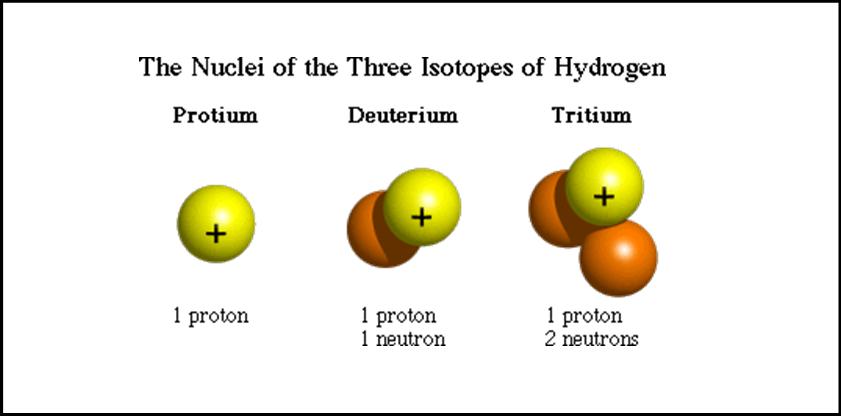
For example, two samples taken from the tombs of two Egyptian kings, Zoser and Sneferu , independently dated to BC plus or minus 75 years, were dated by radiocarbon measurement to an average of BC plus or minus years. These results were published in Science in In nature, carbon exists as two stable, nonradioactive isotopes: The half-life of 14 C the time it takes for half of a given amount of 14 C to decay is about 5, years, so its concentration in the atmosphere might be expected to reduce over thousands of years, but 14 C is constantly being produced in the lower stratosphere and upper troposphere , primarily by galactic cosmic rays , and to a lesser degree by solar cosmic rays.
Once produced, the 14 C quickly combines with the oxygen in the atmosphere to form first carbon monoxide CO , [14] and ultimately carbon dioxide CO 2. Carbon dioxide produced in this way diffuses in the atmosphere, is dissolved in the ocean, and is taken up by plants via photosynthesis.
Animals eat the plants, and ultimately the radiocarbon is distributed throughout the biosphere. The ratio of 14 C to 12 C is approximately 1. The equation for the radioactive decay of 14 C is: During its life, a plant or animal is in equilibrium with its surroundings by exchanging carbon either with the atmosphere, or through its diet. It will therefore have the same proportion of 14 C as the atmosphere, or in the case of marine animals or plants, with the ocean.
Once it dies, it ceases to acquire 14 C , but the 14 C within its biological material at that time will continue to decay, and so the ratio of 14 C to 12 C in its remains will gradually decrease. The equation governing the decay of a radioactive isotope is: Measurement of N , the number of 14 C atoms currently in the sample, allows the calculation of t , the age of the sample, using the equation above. The above calculations make several assumptions, such as that the level of 14 C in the atmosphere has remained constant over time. The calculations involve several steps and include an intermediate value called the "radiocarbon age", which is the age in "radiocarbon years" of the sample: Calculating radiocarbon ages also requires the value of the half-life for 14 C.
Radiocarbon ages are still calculated using this half-life, and are known as "Conventional Radiocarbon Age". Since the calibration curve IntCal also reports past atmospheric 14 C concentration using this conventional age, any conventional ages calibrated against the IntCal curve will produce a correct calibrated age. When a date is quoted, the reader should be aware that if it is an uncalibrated date a term used for dates given in radiocarbon years it may differ substantially from the best estimate of the actual calendar date, both because it uses the wrong value for the half-life of 14 C , and because no correction calibration has been applied for the historical variation of 14 C in the atmosphere over time.
Carbon is distributed throughout the atmosphere, the biosphere, and the oceans; these are referred to collectively as the carbon exchange reservoir, [32] and each component is also referred to individually as a carbon exchange reservoir. The different elements of the carbon exchange reservoir vary in how much carbon they store, and in how long it takes for the 14 C generated by cosmic rays to fully mix with them.
This affects the ratio of 14 C to 12 C in the different reservoirs, and hence the radiocarbon ages of samples that originated in each reservoir.
Radiocarbon dating
There are several other possible sources of error that need to be considered. The errors are of four general types:. To verify the accuracy of the method, several artefacts that were datable by other techniques were tested; the results of the testing were in reasonable agreement with the true ages of the objects.
Over time, however, discrepancies began to appear between the known chronology for the oldest Egyptian dynasties and the radiocarbon dates of Egyptian artefacts. The question was resolved by the study of tree rings: Coal and oil began to be burned in large quantities during the 19th century. Dating an object from the early 20th century hence gives an apparent date older than the true date. For the same reason, 14 C concentrations in the neighbourhood of large cities are lower than the atmospheric average. This fossil fuel effect also known as the Suess effect, after Hans Suess, who first reported it in would only amount to a reduction of 0.
A much larger effect comes from above-ground nuclear testing, which released large numbers of neutrons and created 14 C. From about until , when atmospheric nuclear testing was banned, it is estimated that several tonnes of 14 C were created.
Radiocarbon dating - definition of radiocarbon dating by The Free Dictionary
The level has since dropped, as this bomb pulse or "bomb carbon" as it is sometimes called percolates into the rest of the reservoir. Photosynthesis is the primary process by which carbon moves from the atmosphere into living things. In photosynthetic pathways 12 C is absorbed slightly more easily than 13 C , which in turn is more easily absorbed than 14 C. This effect is known as isotopic fractionation.
At higher temperatures, CO 2 has poor solubility in water, which means there is less CO 2 available for the photosynthetic reactions.
Navigation menu
The enrichment of bone 13 C also implies that excreted material is depleted in 13 C relative to the diet. The carbon exchange between atmospheric CO 2 and carbonate at the ocean surface is also subject to fractionation, with 14 C in the atmosphere more likely than 12 C to dissolve in the ocean. This increase in 14 C concentration almost exactly cancels out the decrease caused by the upwelling of water containing old, and hence 14 C depleted, carbon from the deep ocean, so that direct measurements of 14 C radiation are similar to measurements for the rest of the biosphere.
Correcting for isotopic fractionation, as is done for all radiocarbon dates to allow comparison between results from different parts of the biosphere, gives an apparent age of about years for ocean surface water. The CO 2 in the atmosphere transfers to the ocean by dissolving in the surface water as carbonate and bicarbonate ions; at the same time the carbonate ions in the water are returning to the air as CO 2.
The deepest parts of the ocean mix very slowly with the surface waters, and the mixing is uneven. The main mechanism that brings deep water to the surface is upwelling, which is more common in regions closer to the equator. Upwelling is also influenced by factors such as the topography of the local ocean bottom and coastlines, the climate, and wind patterns. Overall, the mixing of deep and surface waters takes far longer than the mixing of atmospheric CO 2 with the surface waters, and as a result water from some deep ocean areas has an apparent radiocarbon age of several thousand years.
Upwelling mixes this "old" water with the surface water, giving the surface water an apparent age of about several hundred years after correcting for fractionation. The northern and southern hemispheres have atmospheric circulation systems that are sufficiently independent of each other that there is a noticeable time lag in mixing between the two. Since the surface ocean is depleted in 14 C because of the marine effect, 14 C is removed from the southern atmosphere more quickly than in the north. For example, rivers that pass over limestone , which is mostly composed of calcium carbonate , will acquire carbonate ions.
Similarly, groundwater can contain carbon derived from the rocks through which it has passed. Volcanic eruptions eject large amounts of carbon into the air. Dormant volcanoes can also emit aged carbon. Any addition of carbon to a sample of a different age will cause the measured date to be inaccurate.
Contamination with modern carbon causes a sample to appear to be younger than it really is: Samples for dating need to be converted into a form suitable for measuring the 14 C content; this can mean conversion to gaseous, liquid, or solid form, depending on the measurement technique to be used. Before this can be done, the sample must be treated to remove any contamination and any unwanted constituents. Particularly for older samples, it may be useful to enrich the amount of 14 C in the sample before testing. This can be done with a thermal diffusion column.
Once contamination has been removed, samples must be converted to a form suitable for the measuring technology to be used. For accelerator mass spectrometry , solid graphite targets are the most common, although gaseous CO 2 can also be used.
The quantity of material needed for testing depends on the sample type and the technology being used. There are two types of testing technology: For beta counters, a sample weighing at least 10 grams 0. For decades after Libby performed the first radiocarbon dating experiments, the only way to measure the 14 C in a sample was to detect the radioactive decay of individual carbon atoms. Libby's first detector was a Geiger counter of his own design.
He converted the carbon in his sample to lamp black soot and coated the inner surface of a cylinder with it. This cylinder was inserted into the counter in such a way that the counting wire was inside the sample cylinder, in order that there should be no material between the sample and the wire. Libby's method was soon superseded by gas proportional counters , which were less affected by bomb carbon the additional 14 C created by nuclear weapons testing. These counters record bursts of ionization caused by the beta particles emitted by the decaying 14 C atoms; the bursts are proportional to the energy of the particle, so other sources of ionization, such as background radiation, can be identified and ignored.
See more words from the same year. Encyclopedia article about radiocarbon dating. What made you want to look up radiocarbon dating? Please tell us where you read or heard it including the quote, if possible. Test Your Knowledge - and learn some interesting things along the way. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
There are a lot of chapters in this collection.
One letter makes all the difference. Three terms, three strong options. Comedian ISMO on the complexities of the word 'tip'. Comedian ISMO tries to figure out 'one' and 'two'.